Singapore is at the forefront of integrating advanced technologies into its public transportation system. Particularly, its autonomous bus program is a key initiative in revolutionizing urban mobility. Additionally, a detailed examination of the technical aspects of autonomous buses shows how Singapore is setting global standards for smart transit solutions.
Technical Foundations of Autonomous Buses
Singapore’s autonomous buses incorporate advanced technology to manage the complexities of urban traffic. Each bus is equipped with an array of sensors, such as LiDAR, radar, and stereo cameras. These sensors work together to provide a complete 360-degree view around the vehicle. This integration, known as sensor fusion, is essential for processing data in real-time. It enables the buses to detect and navigate around obstacles, recognize traffic signals, and adhere to road markings. This capability is vital for safely navigating through urban environments by effectively detecting obstacles, recognizing traffic signals, and maintaining the correct lane markings (Land Transport Authority).
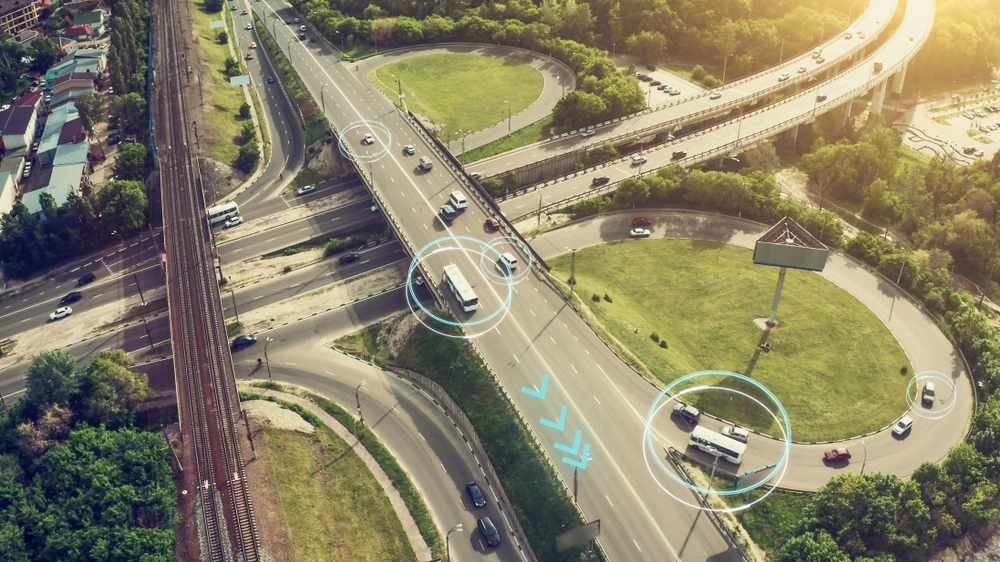
GPS and inertial navigation systems provide precise positioning and routing, essential in the densely built and dynamic urban environment of Singapore. Advanced algorithms process this data to make split-second decisions on speed adjustments, lane keeping, and route changes to ensure safety and efficiency.
Integration of the Autonomous Bus with Traffic Systems
Singapore’s approach integrates autonomous buses into the existing traffic system using V2X (vehicle-to-everything) communication technologies. Firstly, this integration allows buses to communicate with traffic signals and other infrastructure. Consequently, it enhances traffic flow and reduces congestion. Additionally, AI-driven management systems analyze traffic data. These systems then optimize routes and schedules, adapting in real-time to changes in traffic density or road conditions

Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
The autonomous buses in Singapore are electric, aligning with the city’s sustainability goals by reducing carbon emissions. The use of electric vehicles (EVs) in public transit not only supports environmental initiatives but also reduces noise pollution, contributing to a more pleasant urban atmosphere.
Testing and Safety Protocols
Safety is paramount in Singapore’s approach. The country has implemented rigorous testing protocols for autonomous vehicles. Initial tests occur in controlled environments. These then progressively extend to public roads with various traffic conditions. Continuous data collection from these trials helps refine AI models. This ensures the buses respond correctly in all situations (Intelligent Transport).
Simulation technology plays a critical role. It allows developers to model and forecast potential issues in a virtual setting. This helps enhance the bus software before it undergoes road tests.
Public Acceptance and Future Developments
The transition to an autonomous bus system involves public education to build trust in the safety and reliability of the technology. Singapore’s transport authorities conduct public engagement sessions to gather feedback and address concerns, ensuring that the deployment of autonomous buses is met with informed community support.
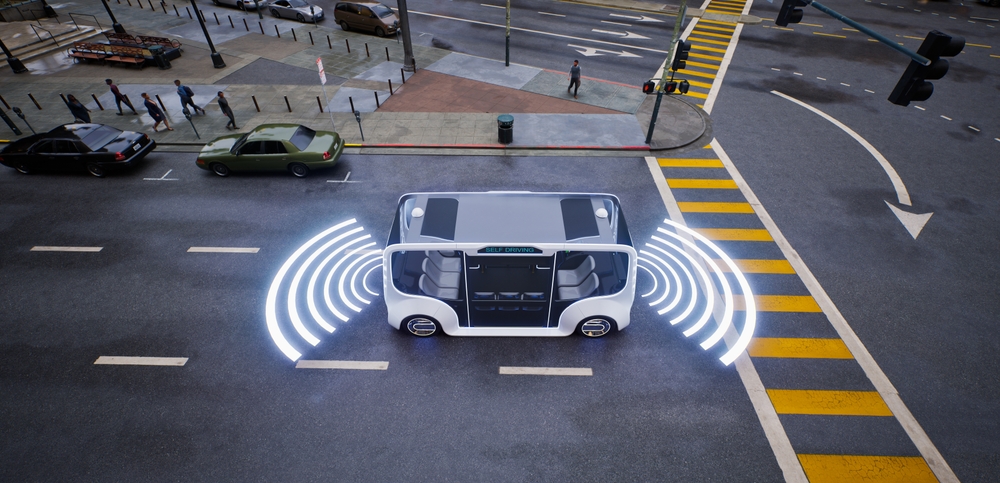

As Singapore expands its autonomous bus program, it not only showcases a commitment to technological innovation but also sets a standard for other cities aiming to modernize their transportation systems. The technical sophistication of these buses promises to enhance the efficiency, safety, and sustainability of public transit, marking a significant step forward in the pursuit of smart, interconnected urban mobility solutions.

